Like other natural ecosystems, the Atlantic Ocean is crucial in regulating global climate conditions. It shapes weather patterns across continents, redistributes heat, and regulates temperatures. Its role in balancing the Earth’s climate is essential since it determines crop production in Africa, sea levels on East Coasts, and weather conditions from the equator to Europe. In spite of that, the Atlantic currents could collapse in approximately the next few years “as from 2025-2095” and affect global climate patterns, food security, and agricultural systems , according to studies from climate scientists and oceanographers
Regulation of global temperatures by the Atlantic Ocean is made possible by the currents referred to as Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC). They are responsible for pushing warm water and precipitation northwards, into the north Atlantic, making their density increase and the temperature decrease. As a result, the water sinks deep, and part of it turns to ice. Subsequently, it rises from the ocean depths while travelling slowly to the Southern Ocean and back to the tropics, thus completing the cycle. The AMOC’s potential collapse could have adverse effects on climate change and agriculture and calls for urgent global action to avoid facing dire consequences like food shortages, displacement of coastal communities, and increased global warming.
Consequences of AMOC’s Collapse on Climate Change and Agriculture
To start with, a collapse would result in extreme climate alterations in both the Southern Hemisphere and the North Atlantic. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the former would experience severe drought due to the retained heat and shift of the rain belt, while the latter would face a decline in temperature by 4 degrees Celsius. In addition, the high temperatures moved by the currents result in mild winters and offer conducive and serine conditions for the marine life’s existence, whoch would also be impacted. The projected changes highlight the vital role played by the AMOC in maintaining biodiversity and moderating temperatures in areas such as Western Europe, Southern Africa, and Central America.
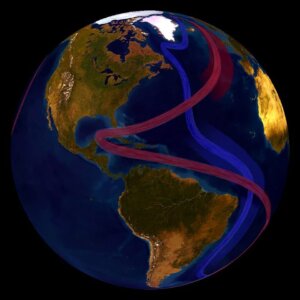
Further, the AMOC is essential in carbon sequestration. It is responsible for transporting vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in the deep ocean. The temperature differences between the equator and the North Atlantic enhance the movement of warm waters and precipitation. The warm surface waters have high concentrations of dissolved carbon dioxide due to the absorption of atmospheric CO2 and biological activities. Consequently, the warm waters moving to the north lose their heat to the atmosphere, becoming more dense and cold, and sinking into the deep ocean where they store CO2 in abyssal layers or carbon reservoirs in the ocean. The sea current’s collapse would result in elevated CO2 levels in the atmosphere, greenhouse effects, and climate change.
The AMOC plays a crucial role in maintaining a balance on sea levels, and its collapse would lead to the rise of coastal lines. The catastrophe could exacerbate the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, thus threatening coastal communities around the globe. According to the National Center for Atmospheric Science’s report, these rising sea levels would affect rain patterns relied on by billions of people practicing agriculture in Asia, the Amazon rainforest in South America, Australia, and central parts of America. Due to the extreme dangers posed by the AMOC’s collapse, authorities must unite in curbing climate change to avoid further distractions on agricultural systems to enhance sustainability, food security, and poverty alleviation among disadvantaged societies.
Moreover, the collapse of the AMOC would affect global agricultural sectors. The currents are essential in the regulation of regional climates through heat redistribution, and their halt would result in intense rainfall and extreme drought in specific areas. Therefore, climate shifts caused by collapsing currents could affect agricultural productivity due to unpredictable weather conditions. Further, AMOC’s collapse would alter the distribution of nutrients and temperature in marine ecosystems, thus affecting marine resources and fish stocks relied on by global coastal communities for economic sustenance. Given these potentially devastating challenges to the farming systems of a significant portion of the planet, there is a pressing need for adaptive actions and strategies.
Actions to Curb the Potential Collapsing of AMOC
Mitigating the potential crisis that could arise with the collapsing of Atlantic currents calls for urgent and coordinated actions from responsible parties globally. Since the collapse could affect marine ecosystems, coastal communities, and weather patterns, intensive approaches that combine international collaboration, scientific research, and policy implementation must be adopted.
Investing in Research
Investing in research is essential in the quest to understand the dynamics of the Atlantic currents. Satellite monitoring, oceanographic studies, and robust data collection are vital in assessing the sea currents’ health, but due to the high costs associated, governments and organizations should also invest in further research. By analyzing the underlying causes of AMOC’s collapse, oceanographers can provide policymakers with essential information to shape effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Promoting International Cooperation
Since the Atlantic currents cut across multiple nations, effective solutions demand international coordination. Transboundary initiatives such as collaborative monitoring, joint research programs, and synergetic policy development would be crucial in achieving positive results. To foster cooperation and dialogue among the associated nations, global forums such as the UN’s conferences on climate change should prioritize AMOC’s concerns and offer a platform to curb the issue collectively.
Sensitize Nations on the Impact of Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs) on AMOC
The most crucial aspect of curbing the AMOC’s collapse is tackling climate change. As per the National Center for Atmospheric Science, the root cause of the Atlantic’s current’s halt is the increase in global temperatures, which are triggered by high greenhouse gas emissions. Global and intergovernmental organizations need to sensitize nations about the impact of greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) on the AMOCs existence. There is also a need to raise more awareness on the significance of pioneering net-zero strategies to mitigate climate change. Strategies to reduce GHG emissions include de-carbonizing industries, sustainable land usage, and adopting renewable energy. In addition, supporting and encouraging international agreements, such as the current climate commitments, would be essential in curbing the untimely effects on Atlantic currents and ensuring joint efforts in fighting climate change are successful
In general, the Atlantic current’s collapse poses a significant global threat to planetary adaptation. As a crucial element of global circulation systems, the AMOC supports marine ecosystems by providing them nutrients and conducive environments, balancing the temperatures between the North Atlantic and the tropics. With international collaboration, reduction in GHG emissions, dedicated scientific research, and marine ecosystem preservation, we can gear towards stabilizing and safeguarding the AMOC’s health. However, the time to act is now , and only through the collaborative efforts of individuals, organizations, and governments can we hope to curb a possible disaster and strive towards sustainable ocean ecosystems.



